Achilles Tendonitis: Everything to Know About This Condition
One of the conditions that our feet and adjacent muscles might suffer is Achilles tendonitis. The condition might not be dangerous initially, but lack of proper care might exacerbate the issue. Learning about Achilles tendonitis is the best way to combat this potential problem. Here is a comprehensive outlook on the condition that provides you with the information you should know.
Overview
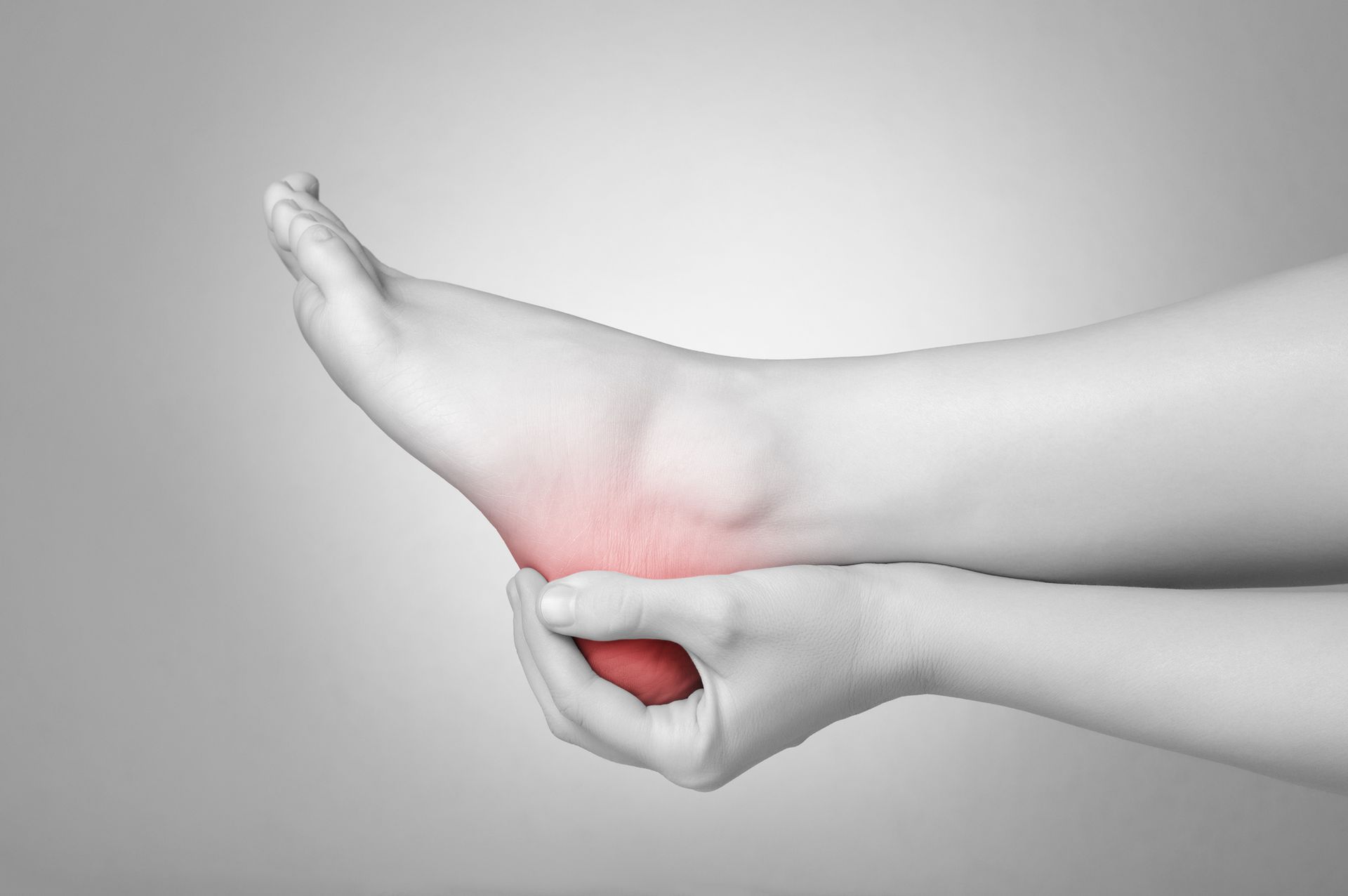
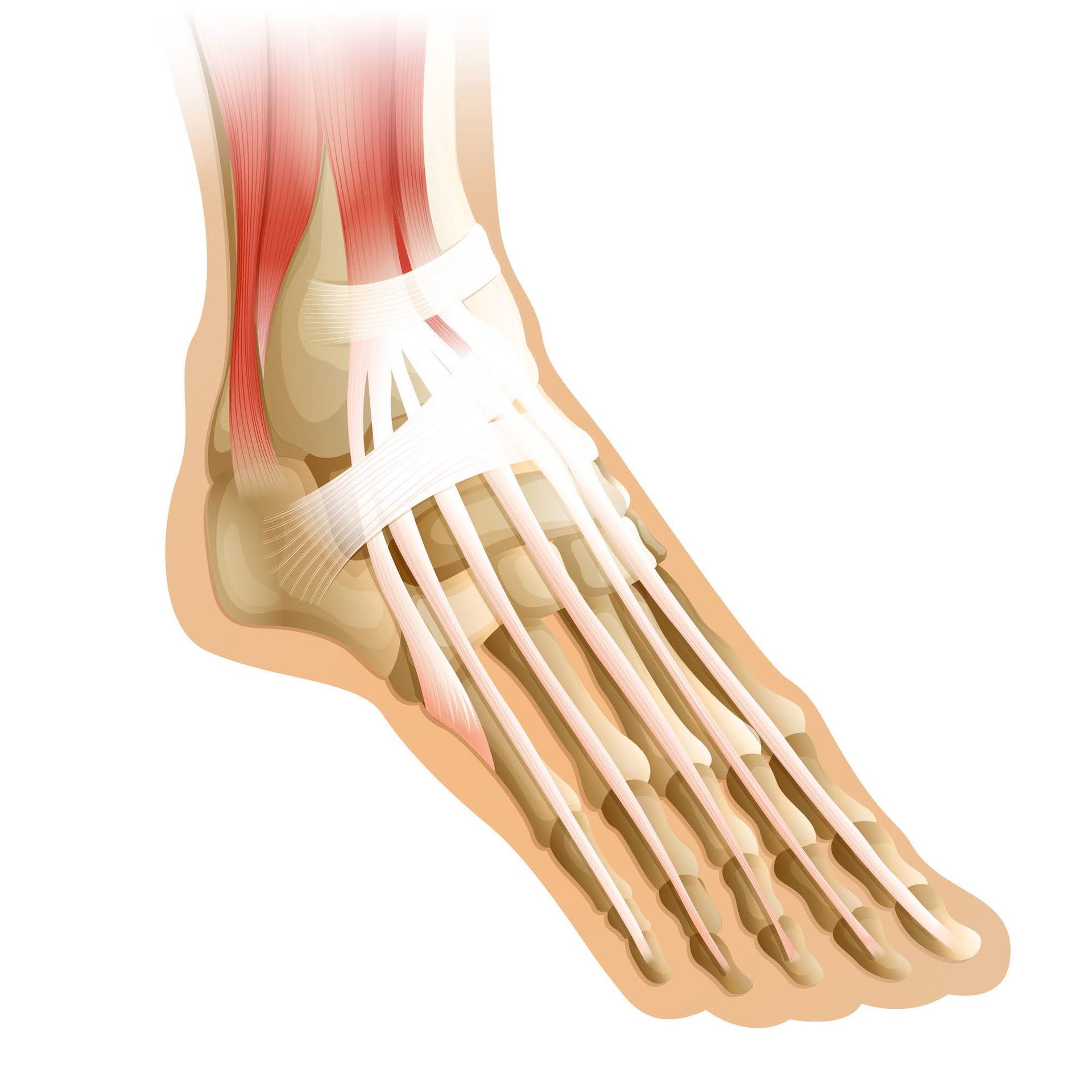
Achilles tendonitis is a condition that affects the Achilles tendon. The Achilles tendon is the large band of tissue that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. You use the Achilles tendon to walk, run, and jump. This is one of the most important tendons in the body.
There are two types of Achilles tendonitis: noninsertional and insertional. Noninsertional Achilles tendonitis involves the middle portion of the tendon. Insertional Achilles tendonitis occurs when the tissue around the insertion point of the Achilles tendon becomes inflamed.
Causes
Achilles tendonitis can occur when the Achilles tendon is overworked or strained. This can happen from participating in sports that stress the Achilles tendon, such as running or basketball. It can also occur from activities that require sudden stops and starts, such as tennis or football.
People at risk to develop Achilles tendonitis participate in sports involving running and jumping. This group includes athletes such as runners, basketball players, and volleyball players. Other risk factors include age, obesity, and having a job requiring repetitive ankle motions.
Other causes include Haglund's deformity and tight calf muscles. Hagland's deformity is a bony growth that forms on the heel bone and can rub against the Achilles tendon and cause irritation.
Symptoms
Achilles tendonitis generates pain in the back of your heel that gets worse with activity. Also, you get stiffness and tenderness in your heel, especially in the morning. You might experience swelling in your heel and difficulty flexing your foot or pointing your toes.
Prevention
You can prevent Achilles tendonitis if you practice the following measures:
- Increase your activity level gradually. If you're new to an exercise program or want to increase your activity level, do so slowly and incrementally. This pace will help your muscles and tendons adjust to the new stresses placed on them and reduce the likelihood of injury.
- Take it easy. Avoid high-impact activities or exercises that place a lot of stress on your Achilles tendon. Instead, opt for low-impact activities like swimming or biking.
- Choose your shoes carefully. Wearing shoes that offer good support and cushioning can help reduce stress on your Achilles tendon. Also, you should avoid high heels.
- Stretch daily. Be sure to stretch your calf muscles and Achilles tendon daily, especially before and after exercise. A simple way to do this is to stand with your feet flat on the ground and then repeatedly rise onto your toes.
- Cross-train. Incorporating various types of exercise into your routine can help reduce the risk of overuse injuries like Achilles tendonitis. These exercises can include swimming, biking, elliptical training, yoga, or Pilates.
Treatment
You can do several things to treat Achilles tendonitis and reduce your risk of developing it. Self-care for Achilles tendonitis includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Patients should also avoid activities that aggravate the condition and focus on gentle stretching and strengthening exercises.
Medications that treat Achilles tendonitis include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen. Therapy interventions include massage and surgery. Orthotics and splints can also support the Achilles tendon and decrease pain.
You should visit a podiatrist for a full diagnosis and medical prescription. If you suspect that you have Achilles tendonitis, vsit us at Advanced Foot Clinic for podiatric services.